· Zen HuiFer · Tutorial · 4 min read
MQTT Practical Combat
Quickly start an MQTT service with Docker and test it using an MQTT client visualization tool

MQTT Practical Combat
This chapter will cover the practical operation of MQTT, mainly including the following contents:
- How to quickly start an MQTT service with Docker
- Basic usage of EMQX
- Using MQTT client visualization tools
- Knowledge related to MQTT topics
Building an MQTT Service
In this section, we will explore how to quickly build an MQTT service using Docker and Docker Compose technology. Docker provides a lightweight, portable containerization solution, while Docker Compose allows us to manage multi-container Docker applications through a simple configuration file.
Building an MQTT Service with Docker
Get Docker Image To start using the MQTT service, you first need to get the Docker image of MQTT. Emqx is a popular open-source MQTT broker, and we can use the following command to get its Docker image:
docker pull emqx/emqx:5.6.1Start Docker Container After getting the image, you can start a Docker container of the Emqx MQTT service with the following command:
docker run -d --name emqx -p 1883:1883 -p 8083:8083 -p 8084:8084 -p 8883:8883 -p 18083:18083 emqx/emqx:5.6.1
This command will start a container instance named emqx and map the different ports of the Emqx MQTT service to the corresponding ports on the host.
Docker Compose Start
To manage the MQTT service more conveniently, especially when deploying a cluster, you can use Docker Compose. First, you need to write a docker-compose.yml file as follows:
version: '3'
services:
emqx1:
image: emqx:5.4.1
container_name: emqx1
environment:
- "EMQX_NODE_NAME=emqx@node1.emqx.io"
- "EMQX_CLUSTER__DISCOVERY_STRATEGY=static"
- "EMQX_CLUSTER__STATIC__SEEDS=[emqx@node1.emqx.io,emqx@node2.emqx.io]"
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "/opt/emqx/bin/emqx ctl", "status"]
interval: 5s
timeout: 25s
retries: 5
networks:
emqx-bridge:
aliases:
- node1.emqx.io
ports:
- 1883:1883
- 8083:8083
- 8084:8084
- 8883:8883
- 18083:18083
emqx2:
image: emqx:5.4.1
container_name: emqx2
environment:
- "EMQX_NODE_NAME=emqx@node2.emqx.io"
- "EMQX_CLUSTER__DISCOVERY_STRATEGY=static"
- "EMQX_CLUSTER__STATIC__SEEDS=[emqx@node1.emqx.io,emqx@node2.emqx.io]"
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "/opt/emqx/bin/emqx ctl", "status"]
interval: 5s
timeout: 25s
retries: 5
networks:
emqx-bridge:
aliases:
- node2.emqx.io
networks:
emqx-bridge:
driver: bridge
This configuration file defines two Emqx MQTT service containers, emqx1 and emqx2, which will communicate through the custom network emqx-bridge and set up health checks to ensure service stability.
After writing the docker-compose.yml file, you can execute the following command in the directory where the file is located to start the service:
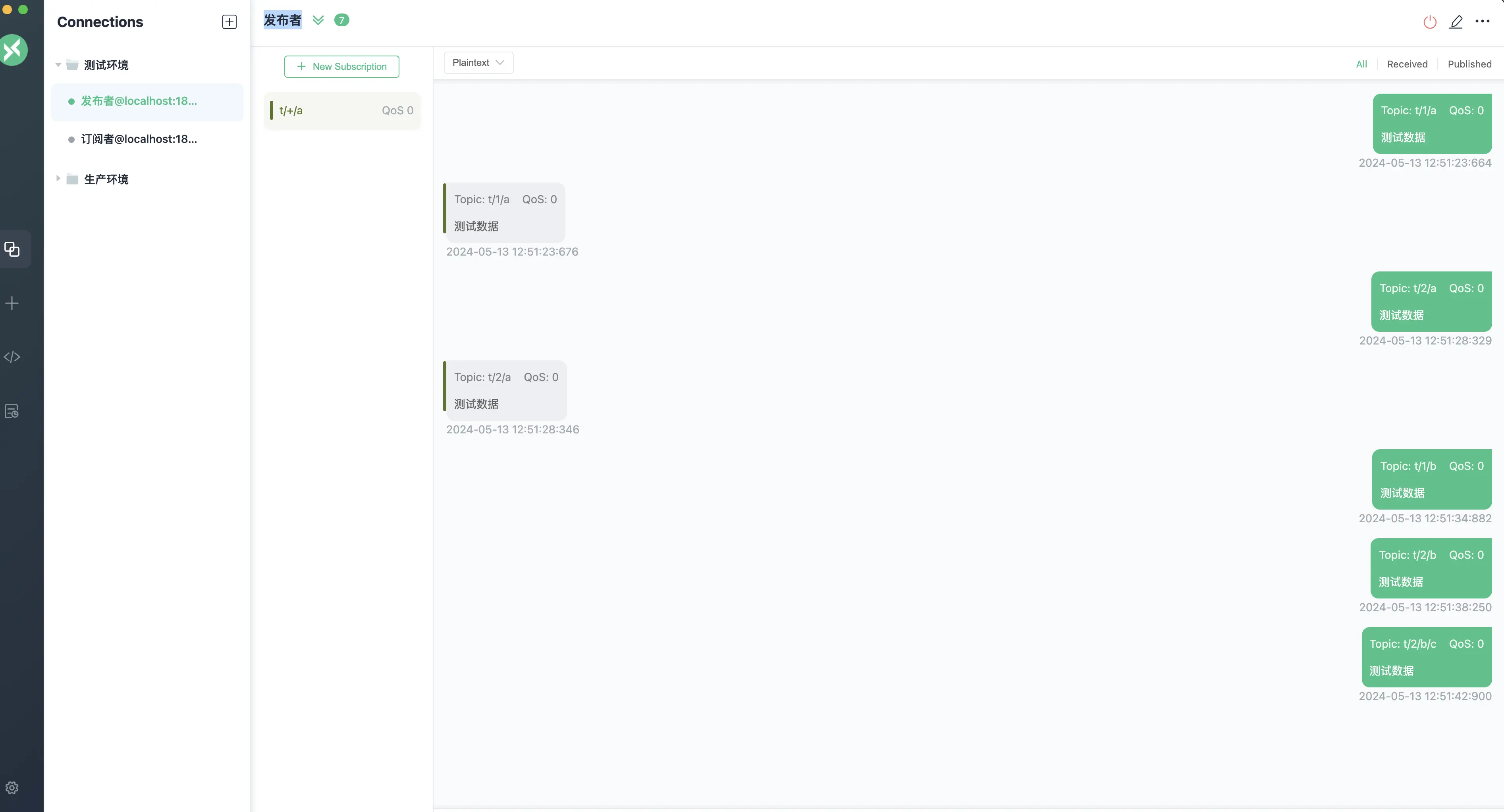
- t/1/a
- t/2/a
- 以及任何符合 t/任意数字/a 模式的其他主题
Now let’s start the actual test, the test case is shown in the figure
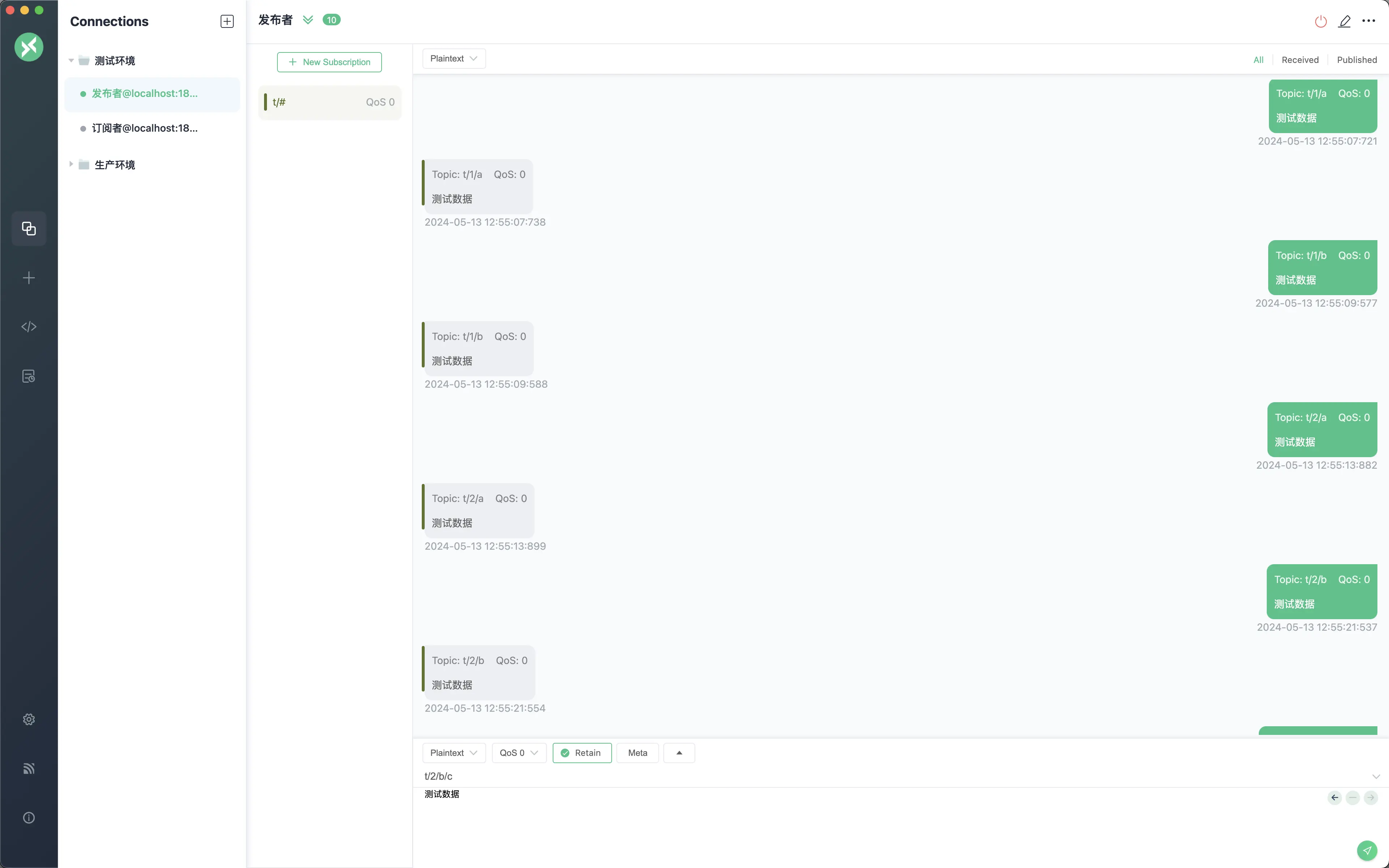
If you want to subscribe to all topics under t, you can use the # wildcard. The specific syntax expression is: t/#
The test case is shown in the figure
System Topics
MQTT system topics start with $SYS/, and they are used in the MQTT protocol to provide information about the MQTT server itself, including running status, statistics, and client online and offline events. These system topics are very useful for monitoring and managing the MQTT service.
System topics can be subscribed to receive updates on the status of the MQTT server. For example, if you want to monitor the status of all nodes in the EMQX cluster, you can subscribe to the $SYS/brokers topic. When the status of any node changes, you will receive an update message.
Common MQTT system topics are shown in the table
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| $SYS/brokers | EMQX cluster node list |
| $SYS/brokers/emqx@127.0.0.1/version | EMQX version |
| $SYS/brokers/emqx@127.0.0.1/uptime | EMQX uptime |
| $SYS/brokers/emqx@127.0.0.1/datetime | EMQX system time |
| $SYS/brokers/emqx@127.0.0.1/sysdescr | EMQX system information |
Topic Naming Rules
In MQTT, topic naming follows certain rules and best practices to ensure topic organization and avoid potential conflicts:
- Avoid using
$SYSas the beginning of the topic: $SYS is a reserved prefix used for system topics, which provide information about the MQTT server itself. - Use
/as the beginning of the topic: It is generally recommended to start topics with /, which helps to clearly identify the beginning of the topic and distinguish it from other parts of the hierarchy. - Avoid using numbers as the beginning of the topic: Although the MQTT protocol does not explicitly prohibit it, it is recommended to start topics with letters or meaningful identifiers to improve readability and manageability.
- **Avoid using share is a special prefix used for shared subscriptions, allowing multiple clients to share subscriptions to the same topic. If shared subscriptions are not needed, this prefix should be avoided.
Examples
Here are some examples of topic names that follow the above rules:
- Correct: home/living_room/temperature
- Correct: sensor/ambient_light
- Incorrect: $SYS/our_temperature (should be reserved for system topics)
- Incorrect: 2nd_floor/temperature (starts with a number)
- Incorrect: $share/our_group_topic (unless used for shared subscriptions)